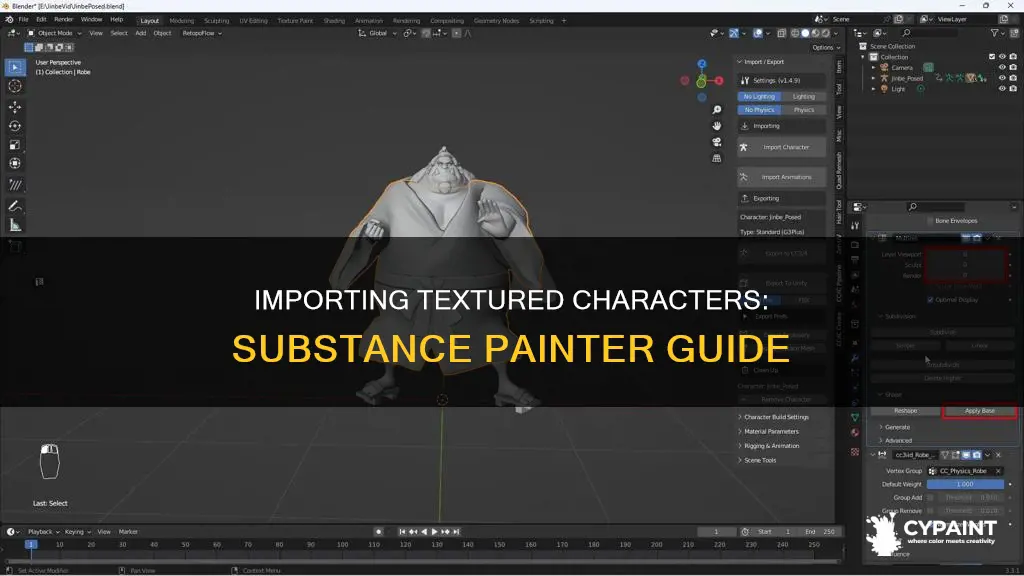
To import a textured character into Substance Painter, you need to first load a texture. Then, designate a UV set by identifying the UDIM number using the UV viewport. Next, enable viewport semi-transparency for the PBR shader. Open the OBJ mesh file and activate the Use UV Tile workflow. Select the Preserve UV Tile layout per material option and enable painting across files. Select OpenGL as the normal map format. Finally, drag your image to the textures shelf, create a fill layer, and drag your texture into the base color.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| File format | OBJ mesh file |
| Workflow | Use UV Tile workflow |
| Texture settings | Add Channels |
| Texture loading | Enable viewport semi-transparency for the PBR shader |
| Texture sets | Multiple UV sets under Std_Skin_Head indicate successful UDIM import |
| Resource storage | Defined by prefix, which can be a folder path |
| Resource naming | Filename indicates the name of the current resource |
| Resource application | Drag images to texture shelf, then make a fill layer and drag texture into base color |
What You'll Learn

Open the OBJ mesh file and activate the Use UV Tile workflow
When importing a textured character into Substance Painter, opening the OBJ mesh file and activating the Use UV Tile workflow is a crucial step. This process allows you to work with multiple UV sets and textures, ensuring a seamless and efficient texturing experience.
To begin, open the OBJ mesh file in Substance Painter. This file contains the 3D model of your character, including its geometry and texture information. Once the file is open, you need to activate the "Use UV Tile" workflow. This workflow enables you to manage and work with UV tiles effectively.
UV Tiles are a powerful feature in Substance Painter that allows you to texture multiple sets of textures across different UV ranges within a Texture Set. By default, without UV Tiles, a texture is repeated over each UV range. However, with UV Tiles enabled, each range becomes a dedicated texture, allowing for higher texture resolution and more detailed work.
To activate the Use UV Tile workflow, follow these steps:
- Open the OBJ mesh file in Substance Painter.
- Go to the Texture Settings and click on "Add Channels."
- Load the desired textures.
- Select the "Preserve UV Tile layout per material" option to ensure that the UV tile layout remains consistent across different materials.
- Enable "painting across files" to give yourself the ability to paint across multiple files if needed.
- Set the "Normal Map Format" to "OpenGL."
By following these steps, you will successfully activate the Use UV Tile workflow, preparing you for the next steps in importing and texturing your character in Substance Painter.
Finding the Perfect Touch-Up Paint for Your 2001 S10
You may want to see also

Designate a UV set and enable viewport semi-transparency
When importing a textured character into Substance Painter, one of the steps involves designating a UV set and enabling viewport semi-transparency. This step is crucial to ensure that the textured character can be properly viewed and edited in the Substance Painter interface.
To begin, you need to open the OBJ mesh file in Substance Painter and activate the "Use UV Tile Workflow." This workflow allows you to preserve the UV tile layout per material and enables painting across multiple files. By selecting OpenGL as the Normal Map Format, you ensure that the UV data is accurately interpreted and displayed.
The next step is to designate a UV set. This involves identifying the UDIM number by utilising the UV viewport. The UV viewport provides a visual representation of the UV layout, making it easier to identify specific UV shells and their corresponding UDIM numbers. Once you have located the desired UV set, you can proceed to the next step.
Enabling viewport semi-transparency is essential for visualising the PBR shader's effect within Substance Painter accurately. Regardless of the viewport settings, semi-transparency will always export properly. This feature ensures that you can see through semi-transparent textures and shaders, aiding in precise texture alignment and editing.
By following these steps, you can successfully designate a UV set and enable viewport semi-transparency. These settings ensure that your textured character is displayed correctly within Substance Painter, providing an accurate foundation for further texturing and painting tasks.
Paint Room: First Day of School Wrap-up
You may want to see also

Click 'Add Channels' inside the texture settings
When importing a textured character into Substance Painter, clicking "Add Channels" inside the texture settings allows you to manage the resolution, channels, and associated mesh maps for the currently selected Texture Set. This is an essential step in controlling the parameters and behaviour of your Texture Set, which is comprised of multiple UV sets.
By clicking "Add Channels", you can create new channels, each with its own specific function. The Base Colour channel, for instance, determines the colour of an object without any lighting or shadow influence. Another channel, Roughness, dictates the reflectiveness of a surface, ranging from shiny to dull. The Metallic channel is also related to reflectiveness, but it is more specific to metallic surfaces.
The Height channel is another important one as it defines depth information and is often used to generate Normal Map detail. This Normal Map is what gives you those wild blue and purple colours you see in Substance Painter. The Height Channel can also be used with displacement maps to add triangle details to an object, which is a more advanced technique.
Additionally, you can create and manage Masks through these channels. Masks are used to show or hide parts of a texture and are usually created in black or white. They are an essential tool in Substance Painter, allowing you to hide everything below a certain layer.
There is also a Substance Painter Python Plugin called TM Channel Manager, which allows you to modify multiple Texture Sets through a simple interface. This can save you time and effort by letting you create, rename, change the format, or delete a Channel across all your Texture Sets simultaneously.
Discovering Artists' Paintings: A Guide to Viewing Locations
You may want to see also

Load a texture
To load a texture in Substance Painter, you must first open the OBJ mesh file and activate the Use UV Tile workflow. You can do this by selecting the "Preserve UV Tile layout per material" option and enabling "painting across files". You should also select OpenGL as the Normal Map Format. Once you see multiple UV sets under "Std_Skin_Head" in the Texture Set list, you'll know that the UDIM data has been successfully imported.
The next step is to load the texture. Start by enabling viewport semi-transparency for the PBR shader to see the effect in Substance Painter. Regardless of your viewport settings, semi-transparency will always export properly.
Now, click on the button in the upper-right corner of the Shader Settings panel, then click on the shader name. Typically, this is a "PBR Metal Rough material". Click on "PBR Metal Rough with Alpha Blending".
Finally, click on "Add Channels" inside the texture settings. The Texture Import template will load multiple images and automatically connect them to the correct output channels based on their filenames. Channel matching is based on specific naming conventions. If there are any duplicates or textures without a match, they will be marked as such in the interface.
Weight Paint Mode Secrets: Hiding Techniques in Blender
You may want to see also

Drag images to the textures shelf, then make a fill layer and drag your texture into base colour
To get started with texturing in Substance Painter, you must first ensure that you have the correct UV information. Go to File > Export > FBX, and in the export window, select the Vertex Colours box. Once you've selected where to save the file, open it in Substance Painter. Make sure Auto-Unwrap is deactivated and your Template is set to Metallic Roughness before clicking OK.
Now, you can begin to drag your images into the Textures Shelf. In the Textures Shelf, scroll down to Roughness, open Textures, and drag in your Roughness Map. You can then add a Metallic layer under Reflection Strength. Go to Layer Colour and drop your Base Colour into the Texture.
Next, go to the Normal tab and input your Normal Map. Finally, go to Displacement and add some height to your textures. It is recommended to start with a low height value to avoid distorting your model.
Importing Diffuse Textures: Substance Painter's Guide
You may want to see also